티스토리 뷰
728x90
반응형
연산자란?
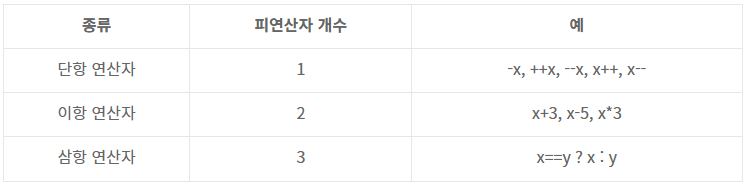
- 연산자는 '연산을 수행하는 기호'를 말합니다. 예를 들어 '+' 기호는 덧샘 연산을 수행합니다
- 연산자가 연산을 수행할려면 연산 대상이 있어야 하는데 연산의 대상을 가리켜 피연산자라고 합니다.
- 10 + 3 연산식에서 +는 연산자이고 10과 3은 피연산자에 해당합니다.

산술 연산자
- 산술 연산의 경우 피연산자의 타입이 다를 경우 값의 손실이 발생할 가능성이 있기 때문에 두 피 연산자의 타입이 일치해야합니다. 그래서 피연산자의 타입이 다르면 형변환을 통해서 타입을 일치시켜줘야 합니다.
- 두 피연산자의 타입 중에서 범위가 더 큰 타입으로 일치시키며 자동적으로 형변환이 되어 형변환 연산자를 생략할 수 있습니다.
- 아래의 코드 중 (float)N / M은 int형인 N을 float형으로 승격시켜 주었기 때문에 /(나누기) 연산자를 사용해도 값 손실이 발생하지 않습니다.
- 다만 (float)(N + M)의 경우는 int형끼리 먼저 나누고 float형으로 승격을 해주었지만 연산과정에서 값 손실이 발생하였습니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 10;
int M = 4;
System.out.println(N + M); // 14
System.out.println(N - M); // 6
System.out.println(N * M); // 40
System.out.println(N / M); // 2
System.out.println((float)N / M); // 2.5
System.out.println((float)(N / M)); // 2.0
}long + int -> long + long -> long
float + int -> float + float -> float
double + float -> double + double -> double
비트 연산자
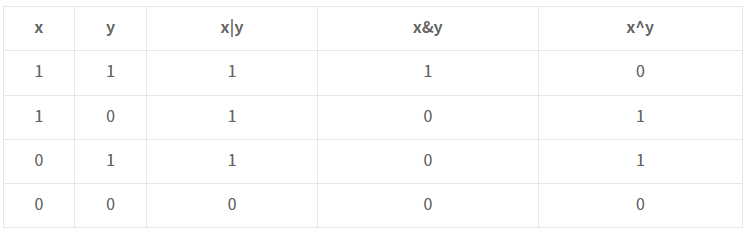
- 비트 연산자는 피연산자를 비트 단위로 논리 연산을 합니다.
- |(OR 연산자) - 피연산자중 하나라도 1이 있다면 1, 아니면 0
- &(AND 연산자) - 피연산자중 둘 모두 1이면 1, 아니면 0
- ^(XOR 연산자) - 피연산자 값이 서로 다른 경우면 1, 아니면 0
instanceof
- 객체가 특정 클래스 / 인터페이스 유형인지의 여부를 확인합니다.
- 객체 타입을 확인하는데 사용하는 연산자로 해당 여부를 true, false로 알려줍니다.
- 어떤 타입에 대한 instanceof의 연산 결과가 true이면 해당 타입으로 형변환이 가능합니다.
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
System.out.println(child instanceof Child); // true
System.out.println(child instanceof Parent); // true
System.out.println(child instanceof Object); // true
}
}
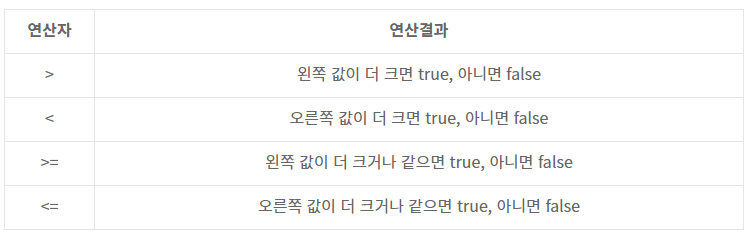
관계 연산자
==
- 두 값이 같으면 true, 다르면 false를 리턴합니다.
Case 01 - Primotove 타입
public static void main(String[] args) {
int one = 1;
int ONE = 1;
int two = 2;
System.out.println(one == ONE); // true
System.out.println(one == two); // false
}Case 02 - Reference 타입
- 리터럴인 경우
- 아래의 코드를 보시면 hello1과 hello2 두 변수의 == 연산의 결과로 true인 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- String 변수에 동일한 리터럴을 대입하게 되면 String Constant Pool에 저장이 되어서 같은 주소의 값을 가지게 됩니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hello1 = "Hello";
String hello2 = "Hello";
System.out.println(hello1 == hello2); // true
System.out.println(hello1.equals(hello2)); // true
}- 생성자로 생성한 경우
- hello1과 hello2는 new 키워드와 생성자를 사용하여 객체를 생성하게 되면 서로 다른 주소값을 가지게 되므로 == 연산의 결과로 false를 반환하게 됩니다.
- 이럴 경우는 주소가 아닌 해시코드 값(객체의 내용물)을 비교해주는 equals() 메서드를 사용하여 비교해야 합니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hello1 = new String("Hello");
String hello2 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(hello1 == hello2); // false
System.out.println(hello1.equals(hello2)); // true
}
논리 연산자
- 논리 연산자는 둘 이상의 조건을 '그리고', '나', '또는' 으로 연결하여 하나의 식으로 표현할 수 있습니다.
- ||(OR) - 피연산자 중 어느 한쪽만 true이면 true를 반환합니다.
- &&(AND) - 피연산자 양쪽 다 true여야만 true를 반환합니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int zero = 0;
int one = 1;
int two = 2;
System.out.println(one < two || one < zero); // true
System.out.println(one < two && one > zero); // true
System.out.println(one > two && one > zero); // false
}
assignment(=) operator :: 대입 연산자
Case 01 - Primotove 타입
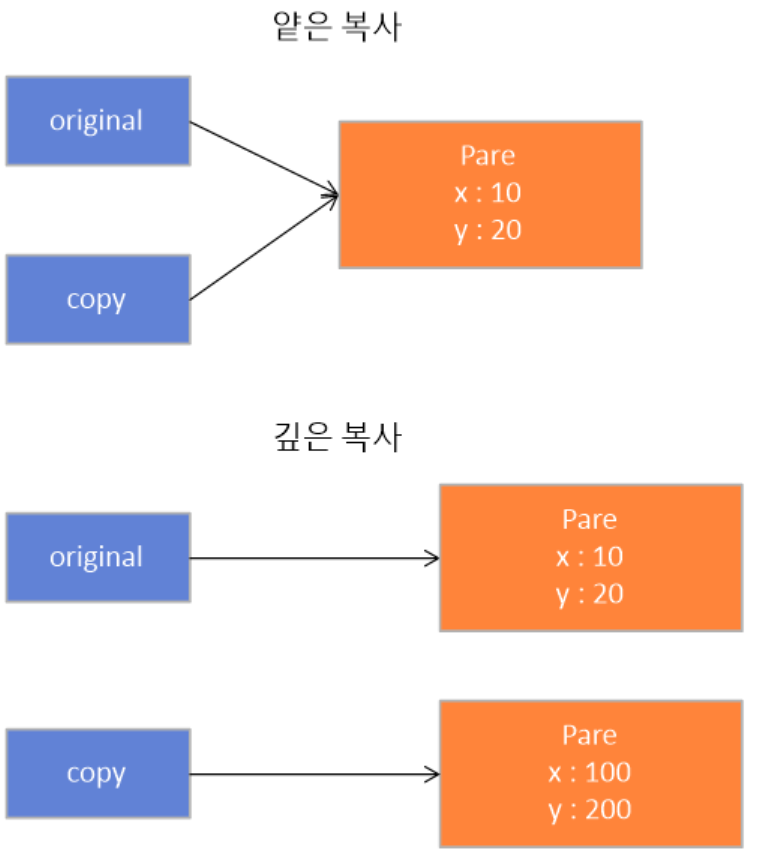
- 아래와 같이 copy라는 변수에 original을 대입하여도 깊은 복사가 이루어지기 때문에 원래의 값에는 지장이 없습니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int original = 10;
int copy = original;
System.out.println(original); // 10
System.out.println(copy); // 10
copy = 20;
System.out.println(original); // 10
System.out.println(copy); // 20
}Case 02 - Reference 타입
- 복사한 값이 변경되면 원래의 값도 변화가 발생하는 얕은 복사가 이루어 집니다.
static class Pare {
int x;
int y;
public Pare(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pare original = new Pare(10, 20);
Pare copy = original;
System.out.println("x : " + original.x +", y : "+ original.y); // x : 10, y : 20
System.out.println("x : " + copy.x +", y : "+ copy.y); // x : 10, y : 20
copy.x = 100;
copy.y = 200;
System.out.println("x : " + original.x +", y : "+ original.y); // x : 100, y : 200
System.out.println("x : " + copy.x +", y : "+ copy.y); // x : 100, y : 200
}
화살표(->) 연산자
- 화살표(->) 연산자는 자바8의 람다식 도입으로 생겨나게 되었습니다.
- 람다식은 메서드를 하나의 식으로 표현함으로써 함수를 간략하고 명확한 식으로 표현할 수 있도록 해줍니다.
- 화살표 연산자는 인터페이스의 추상 메서드 구현을 간단하게 구현할 수 있도록 도와주는 역할을 합니다.
- 인터페이스를 클래스를 만들지 않고 바로 사용하기 위한 방법으로는 익명 객체로 추상 메서드를 구현할 수 있습니다. 그런데 이러한 코드를 더욱 더 간편하게 줄여줄 수 있습니다.
익명 객체를 사용하여 추상 메서드 구현
public class Example {
public interface AddInterface{
public int add(int a,int b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddInterface addInterface = new AddInterface() {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
};
System.out.println(addInterface.add(10, 30)); // 40
}
}
화살표 연산자를 이용하여 간편하게 구현
public class Example {
public interface AddInterface{
public int add(int a,int b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddInterface addInterface = (a, b) -> {return a + b;};
System.out.println(addInterface.add(10, 30));
}
}
3항 연산자
조건식 ? 반환값1 : 반환값2
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
int result;
result = 1 > 0 ? x : y; // 5
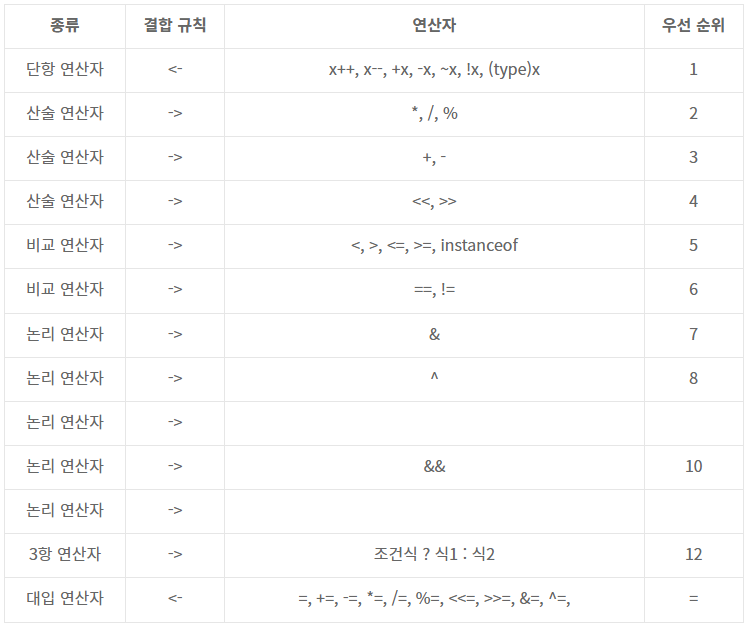
연산자 우선 순위
- 산술 > 비교 > 논리 > 대입 순으로 우선순위가 높습니다.
- 단항 > 이항 > 삼항 순으로 우선순위가 높습니다.
- 단항 연산자와 대입 연산자를 제외하고는 연산의 진행방식이 왼쪽에서 오른쪽입니다.
728x90
반응형
'JAVA > JAVA기본' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA - hashCode의 의미 (1) | 2021.12.14 |
|---|---|
| JAVA - (optional) Java 13, switch 연산자 (0) | 2021.12.14 |
| JAVA - 불변객체(Immutable Object)란(feat.final)? (0) | 2021.12.12 |
| JAVA - Wrapper Class란? (0) | 2021.12.10 |
| JAVA - 변수 (feat.스코프와 라이프 타임 & 타입 변환, 캐스팅, 프로모션) (0) | 2021.12.08 |
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
TAG
- spring boot excel download oom
- space based architecture
- spring boot 엑셀 다운로드
- @ControllerAdvice
- 자바 백엔드 개발자 추천 도서
- 람다 표현식
- java userThread와 DaemonThread
- 레이어드 아키텍처란
- redis 대기열 구현
- 서비스 기반 아키텍처
- spring boot redis 대기열 구현
- microkernel architecture
- JDK Dynamic Proxy와 CGLIB의 차이
- redis sorted set으로 대기열 구현
- redis sorted set
- java ThreadLocal
- pipe and filter architecture
- transactional outbox pattern
- spring boot poi excel download
- 트랜잭셔널 아웃박스 패턴 스프링 부트 예제
- service based architecture
- spring boot redisson sorted set
- pipeline architecture
- spring boot redisson destributed lock
- spring boot redisson 분산락 구현
- 트랜잭셔널 아웃박스 패턴 스프링부트
- polling publisher spring boot
- transactional outbox pattern spring boot
- 공간 기반 아키텍처
- spring boot excel download paging
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
